blog 2021 5 min read
Cluster rendering: The tech that makes it possible

From projecting dazzling visuals up the sides of skyscrapers to creating sprawling virtual film sets and immersive live events, cluster rendering looks set to turn multiple industries on their heads. But how does it work - and what technology lays behind its near unlimited potential?
This new disguise feature developed in partnership with Epic Games allows visuals on any scale to be rendered to a higher standard than ever before. This is done by splitting Unreal Engine content into fragments that are each rendered by different disguise machines, increasing the overall render power of your content.
The impact of this is instantly noticeable - gone is the need to choose between groundbreaking graphics and large-scale visibility. Gone are concerns about latency issues as projects outgrow the limited processing power of an individual machine. Instead, users looking to create high-fidelity, photorealistic imagery are limited only by what they can imagine.
Let’s explore the technology that makes cluster rendering possible.
The Hardware
Two pieces of hardware live at the centre of disguise’s cluster rendering solution - the disguise vx server, and the rx nodes.
The vx server is available in a number of models, allowing users to select the unit that best serves the needs of their production. With a varying number of outputs, each unit offers interchangeable connection points to best ensure compatibility with your existing equipment.
The vx servers are engineered to playback video of the highest quality and at any scale. They also act as your access point to the disguise software, giving you full control over every element of your visual designs.

Paired with the server are disguise’s rx nodes that will each take on the rendering of specific fragments of the overall end product. This means that each element is given the processing power it needs to ensure high-fidelity results regardless of what you’re creating.
Each node works as part of the wider network, and acts as the hosting platform for Unreal Engine content, to bring the latest in rendering technology to your production.

The Software
Supporting the vx and rx units is disguise’s custom-built RenderStream infrastructure, enabling cluster rendering however suits your needs. The RenderStream protocol has been specifically created to ensure the smoothest of experiences, with low latency and high-fidelity results that bring your content to life.
The new disguise r18 software makes the realisation of cluster rendering easier than ever. The release provides the most advanced integration of Unreal Engine to date, allowing you to load up and manipulate Unreal environments from the disguise timeline, in whatever way best suits your production.
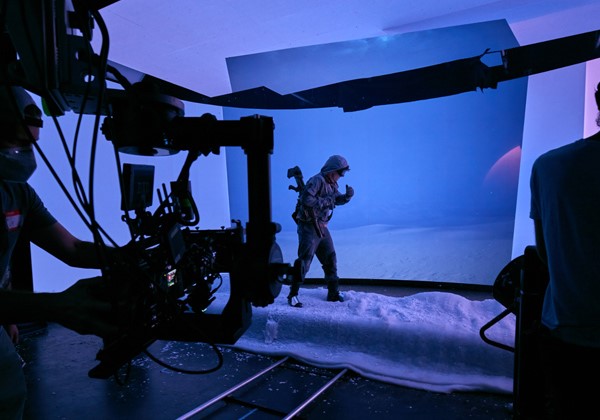
Below we can see a potential cluster rendering set-up. The vx unit sits at the centre, acting both as the output that brings rendered footage to fruition and as the central hub through which users can control their designs and connect with every element of the process. The vx unit is able to communicate bidirectionally, allowing you more flexibility. Virtual and extended reality (xR) productions like this can benefit from tracking camera movements and changing the scenery accordingly for extra realistic shots.
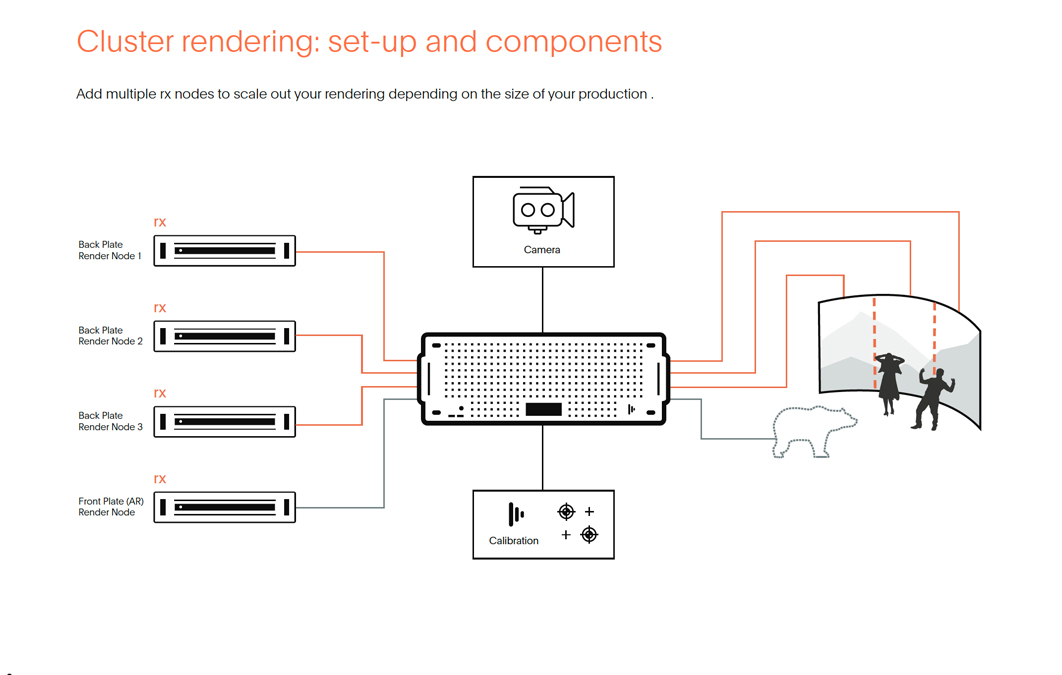
The four rx nodes on the left of this diagram are each responsible for different fragments of the overall scene render. In this case, the director has split the virtual production backdrop over three sections, each rendered by a different node. This enables high-quality renders unhampered by a single node’s processing limitations, whilst RenderStream’s colour calibration techniques ensure no visible transition from one cluster to the next.
In front of both the backdrop and the on-set actors, an augmented reality (AR) grizzly bear is overlaid seamlessly, rendered by the fourth rx node, ensuring each hair on his back is given the attention it requires.
Flexible Variations
Cluster rendering is not limited to the above set-up. Whatever your project, the combination of RenderStream and disguise’s vx and rx units will allow you to find a scenario that best suits your needs.
In the above diagram, the digital canvas was split into thirds, and each section was designated an rx node. But others might find it more useful to split the overall render in a different way. It’s also possible, for instance, for users to cluster by objects. The distant backdrop - a mountain range, or sky and clouds - can be rendered by one node, whilst elements in the foreground are rendered by another. This makes it easy for powerful renders that enable you to change the weather, or even the position of the mountains whilst keeping the immediate scenery in the foreground exactly as it was.
xR environments can be part of a render cluster too, broken down into different plates. Again, the background can be rendered by one rx node - perhaps creating a state-of-the-art digital studio from which a news broadcast can be presented. Producers can then utilise a different node to render overlaid AR elements. Whilst one enables digital recreations of extreme weather to demonstrate the risk to the public, another might enable more simple text giving specific information. Any scenario can be imagined to specifically fit the needs of your project.
From the rx and vx units to disguise’s RenderStream and software, every inch of your cluster rendering needs have been accounted for. Now you can create anything you can imagine on any scale, giving you free rein to render the most incredible visions. Find out more about what disguise’s cluster rendering solutions can do for you today.

